Imagine manually managing thousands of assets every day while worrying about impending loss, theft, and misallocation of resources. What if you lose a machine worth thousands of dollars? No matter how big or small, loss and theft can significantly harm business operations and lead to high levels of inefficiency.
Manual data processing can affect the quality of asset details collected and magnify losses; record fragmentation and missing information are some of the reasons why asset data quality deteriorates. For example, according to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of approximately $12.9 million per year.
To avoid situations like this, it’s in your organization’s best interest to automate the asset tracking process using a modern GPS asset tracking system. With the rapid advancement of technology, many organizations now prefer to utilize GPS tools to help track asset movement and provide real-time data.
This blog will introduce you to GPS asset tracking, its related use cases, and how it can help transform your asset management processes.
What is GPS asset tracking?
GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a means of tracking the movement of items through satellite signals. GPS is part of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and provides geographic location and time information for any asset you wish to track using a GPS receiver. Trackers connect to physical devices and signal the device’s exact location to your internal systems.
Location data is transmitted to GPS for real-time location monitoring. This helps maintain detailed records of asset data and ensures your assets don’t sit idle unnecessarily. There are many types of GPS trackers for asset management, two of which are:
- Asset GPS Tracker: Used to monitor the location and movement of assets such as vehicles, containers, heavy machinery, etc. GPS trackers can be applied to any type of asset as long as the tracker is securely applied and secured.
- Car GPS locator: Vehicle trackers can be applied to any vehicle to track when the vehicle leaves a specific location. Businesses can connect these trackers with asset management systems to maintain a comprehensive record of asset movement.
Asset tags along with GPS trackers help seamlessly track asset details. You can embed GPS information within asset tags so that the information is available with a simple scan.
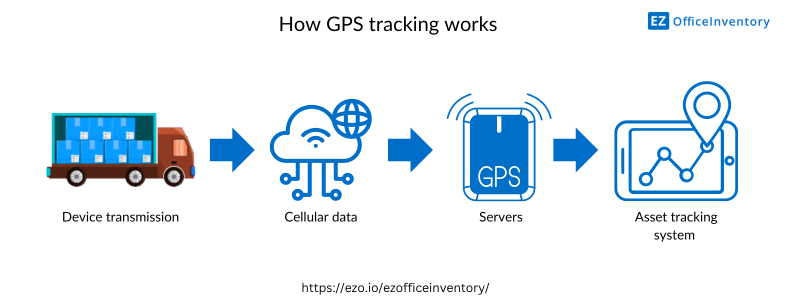
What is the relationship between asset management and GPS asset tracking?
GPS asset tracking is revolutionary in the world of asset management because it provides a deeper understanding of your assets and their operational status. Asset tracking and GPS go hand in hand – one of the main purposes is to reduce the risk of loss and theft. It simply eliminates the need to manually track assets by automating asset tracking.
GPS tracking helps you better manage your asset needs and improve response times to emergencies. For example, a hospital can track the location of an ambulance simply by installing a GPS tracker on it. GPS will send updated information to your asset management system of choice so you can quickly assess whether an ambulance is currently available.
Asset management can systematically catalog assets, and GPS tracking can help use this information to track the whereabouts of assets. GPS tracking depends on efficient asset management; it leverages existing asset records to track an asset’s status, location, and usage. You can easily assess the routes your assets travel most so you can make timely maintenance decisions.
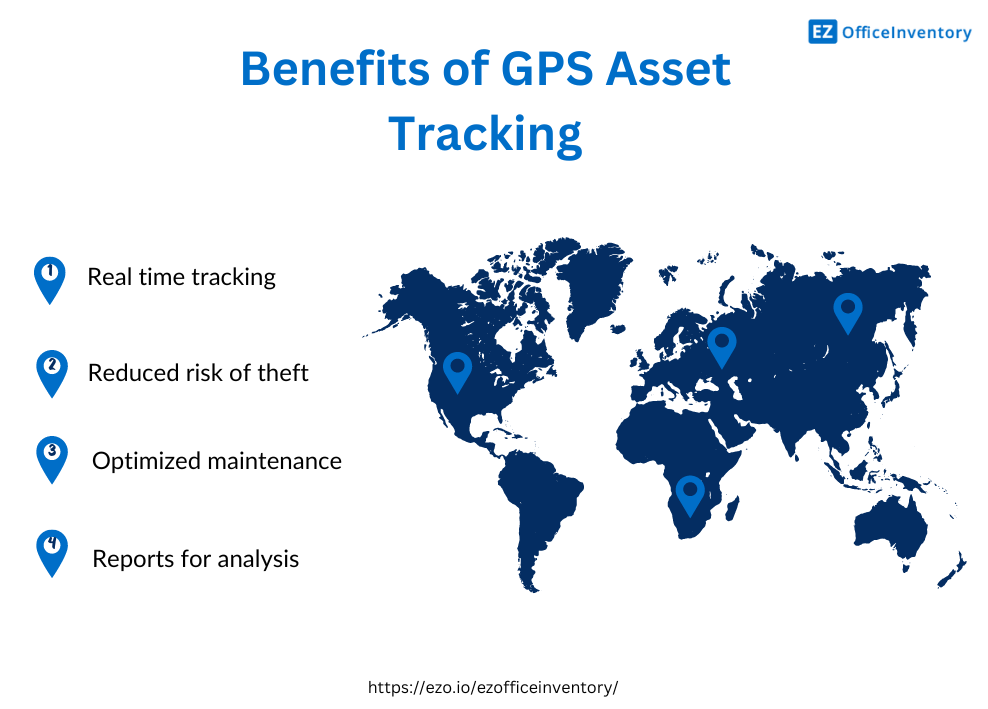
What are the benefits of GPS asset tracking?
By 2025, the GPS asset tracking market size will reach US$3.38 billion, with a compound annual growth rate of 11.58%. The GPS asset tracking market is highly competitive and requires more innovative and technologically advanced tracking technologies. However, as asset management proliferates and the need for real-time data increases, GPS asset tracking has become widely adopted.
GPS trackers often come with enhanced features, including improved accuracy and offline tracking. Here’s how GPS asset tracking helps organizations achieve high visibility of their assets:
1. Real-time tracking
You can integrate your asset tracking system with a GPS tracker to easily reflect and leverage location data. With a GPS tracker, you can receive minute-by-minute information on the movement of your assets and how often their locations change. GPS devices can provide accurate GPS coordinates: longitude and latitude. The latest timestamp of the GPS location is also highlighted so users know when it was updated.
As time and location are updated, the latest asset locations can be instantly pushed to the system’s digital map. Viewing the location of assets on a map improves visibility and enhances visual understanding. For example, you can check if your assets have arrived at a specific office/site by simply checking your location map and zooming in/out to better focus on a specific item.
Location tracking helps optimize asset allocation and resolve any operational issues related to assets. You can assess at a glance what assets are available in a specific location and their details, making it easier to make informed decisions about their allocation. Timely location tracking also optimizes your overall asset management process because you know where and how your assets are being used.
One study showed that 90% of businesses use some type of cloud-based system to track assets.
2. Reduce the risk of theft
GPS tags reduce the likelihood of assets being stolen or lost. With tracking technology, assets can be easily tracked and recovered, enhancing asset security. If an asset is still lost/stolen, you can track its last updated location and recover it immediately. Likewise, automatic alerts can be generated immediately if an asset leaves certain premises – a tracking technology called “geofencing”. Geofencing improves asset security by preventing unauthorized movement of assets.
Not only that, but you can ensure your assets are following the right route. If a driver takes a detour, you can trigger an alert. Unless the asset is moved to a remote location, there is a small chance that you will lose the GPS signal. GPS has extensive coverage, which means you will likely have 24/7 access to the latest location of your assets. This reduces any vulnerabilities in asset tracking and provides a trustworthy device for GPS-based asset management.
3. Optimize maintenance
Once you have complete data on where an asset is and how long it has been in use, you can determine if the asset needs maintenance. For example, if a truck has traveled a long distance, you can look at a map to evaluate its route and whether it is likely to have significant wear and tear, and then you can decide whether to send it in for repairs when you return. –
With a well-functioning GPS tracking system, you can also determine the most time- and fuel-efficient routes for your assets to reduce wear and tear. This helps increase asset utilization and optimize fuel consumption.
You can develop better asset control by evaluating when to check assets back in. This way you can reserve assets for maintenance in advance so that they are not unavailable when needed and cannot be used for any other activity during maintenance.
Users can collect data on device usage and mileage to determine their usage. This encourages proactive maintenance.
4. Report promptly
You can easily generate detailed location reports to optimize asset usage and evaluate where and how assets are used. Asset management systems can receive data from GPS trackers and integrate that information in an easy-to-understand manner.
Simply generate reports on asset condition, location and status to get complete information on how your assets are being used. You can generate reports on asset scan history to evaluate the source of scanned assets and their IP addresses. This way you know the exact location of the last scan performed on the asset, helping to ensure that the asset is in a safe location.
Additionally, you can collect latitude and longitude data from GPS devices and display this data in reports. For example, weekly reports detail which assets have been checked out to different sites and their current longitude and latitude.
You can generate graphs and charts to evaluate which sites have the highest check-in/check-out rates. These charts help make better decisions about asset utilization and resource management.
Use cases for GPS asset tracking
GPS is the smart choice for asset location tracking. Not only does it increase asset security, it also improves day-to-day asset management processes. Here are the top industries using GPS asset tracking systems to enhance asset visibility:
| industry | Example |
|
health care |
Use GPS trackers to check the real-time location of medical equipment such as ventilators, wheelchairs, infusion pumps, and MRI machines. Understand which branches of the same hospital are using available resources. High-priced medicines, such as COVID-19 vaccines, can be tracked across locations to ensure they arrive safely at their destination. |
| educate | School administrators can track school buses to evaluate their routes and optimize pick-up and drop-off schedules. |
| Audiovisual and media | Track assets across different entertainment activities to ensure their timely recovery. Optimize resource allocation, efficiently manage assets for different projects, and purchase additional resources in advance. |
| put up | Get real-time location data on Google Maps for expensive, heavy machinery and equipment that’s constantly moving around job sites. |

Alternative tagging solutions for GPS trackers
While GPS Asset Tracking has revolutionized asset tracking, other tagging solutions also offer viable solutions to your asset tracking needs. These include:
1. Barcode and QR code
You can use an asset management system to generate custom barcode and QR code labels based on the value and type of asset. Barcodes and QR codes embed detailed asset information that you can easily access by scanning.
Furthermore, barcodes serve as item identifiers and can store large amounts of information, i.e. up to 7000 characters.
2. RFID technology
RFID uses radio waves to receive signals and transmit the information to a tracking system. These tags can include data from the asset’s name and identification number to its purchase date and history. You can seamlessly track a large number of assets using RFID tags to automate the data collection process, help monitor inventory levels, and reduce theft in the field.

Improve business efficiency with a state-of-the-art GPS asset tracking system
Timely asset tracking using the latest technology is the need of the hour. Almost every business/organization these days is adapting to the ever-changing technology landscape.
An asset tracking strategy designed to achieve long-term goals is key to achieving greater business efficiency. Asset location tracking plays a key role in ensuring streamlined operations. Set up your asset tracking system today to better manage asset location.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How does GPS tracking help monitor assets?
You can attach GPS trackers to your assets, connect them with asset tracking systems, and monitor assets to ensure they are being used to their maximum capacity.
2. How to integrate GPS tracker with third-party tracking systems?
API integration is one of the most well-known and feasible methods of integrating GPS trackers with third-party asset tracking systems. You simply install the integration and push the asset’s location coordinates to the system and Google Maps for display.
3. What are the three main ways to use GPS location tracking?
3 main ways to leverage the full potential of GPS tracking include:
- Location: Find the exact location of the asset.
- Tracking: Monitor assets in transit and analyze their movements.
- Mapping: Pinpoint asset locations on a map for easy visualization and identification.